Cold storage containers play a vital role in the food and beverage industry, forming the backbone of modern cold chain logistics. These containers provide controlled environments that maintain precise temperature and humidity levels, ensuring the freshness, quality, and safety of perishable goods during storage and transportation. As global trade in perishable products increases, cold storage containers have become an indispensable tool for producers, distributors, and retailers alike.
Content
- 1 1. Temperature Control for Perishable Goods
- 2 2. Preservation of Product Quality and Shelf Life
- 3 3. Support for Multi-Stage Supply Chains
- 4 4. Flexible Storage Solutions for Seasonal Demand
- 5 5. Specialized Storage for Different Food Categories
- 6 6. Compliance with Food Safety Regulations
- 7 7. Integration with Smart Monitoring Systems
- 8 8. Energy-Efficient and Eco-Friendly Refrigeration Systems
- 9 9. Mobility and Rapid Deployment
- 10 10. Role in Emergency and Event Catering Logistics
- 11 Conclusion
1. Temperature Control for Perishable Goods
The primary function of a cold storage container is to maintain the required temperature for sensitive food and beverage products throughout transportation and storage. Depending on the cargo, containers can operate within a wide temperature range—from deep freezing at –25°C for meat and seafood to chilled storage between 0°C and 5°C for fruits, vegetables, and dairy products.
Each container is equipped with a reliable refrigeration system that regulates internal temperature, preventing spoilage caused by heat exposure or bacterial growth. The ability to sustain a constant temperature during long-distance transport ensures that products arrive in optimal condition.
2. Preservation of Product Quality and Shelf Life
Freshness is a major concern in the food and beverage industry. Cold storage containers minimize the natural degradation process by keeping products at ideal temperatures immediately after harvest, processing, or packaging. For example, fruits and vegetables remain crisp and nutritious, while meat products retain their texture, flavor, and color.
By slowing down microbial activity and enzymatic reactions, these containers effectively extend the shelf life of perishable goods, reducing waste and enhancing market value for both domestic and international shipments.
3. Support for Multi-Stage Supply Chains
Modern food logistics involves multiple stages—from farms and fisheries to processing plants, distribution centers, and retail outlets. Cold storage containers serve as mobile and modular cold rooms that can be deployed at each stage of the supply chain.
- At the production site, containers store harvested produce or processed food before transport.
- During transit, they maintain consistent conditions on ships, trucks, or trains.
- At distribution hubs, containers act as temporary cold storage units awaiting further dispatch.
This continuity of temperature management across all stages is what makes cold storage containers essential for maintaining an unbroken cold chain.
4. Flexible Storage Solutions for Seasonal Demand
The food and beverage industry often experiences seasonal surges in demand—such as during holidays, harvest seasons, or export peaks. Cold storage containers offer a flexible solution to expand refrigeration capacity temporarily without the need for permanent facilities.
Companies can rent or deploy additional containers at processing plants, ports, or retail centers to handle overflow inventory. Once demand subsides, the containers can be easily relocated or decommissioned, minimizing long-term costs while maintaining operational efficiency.
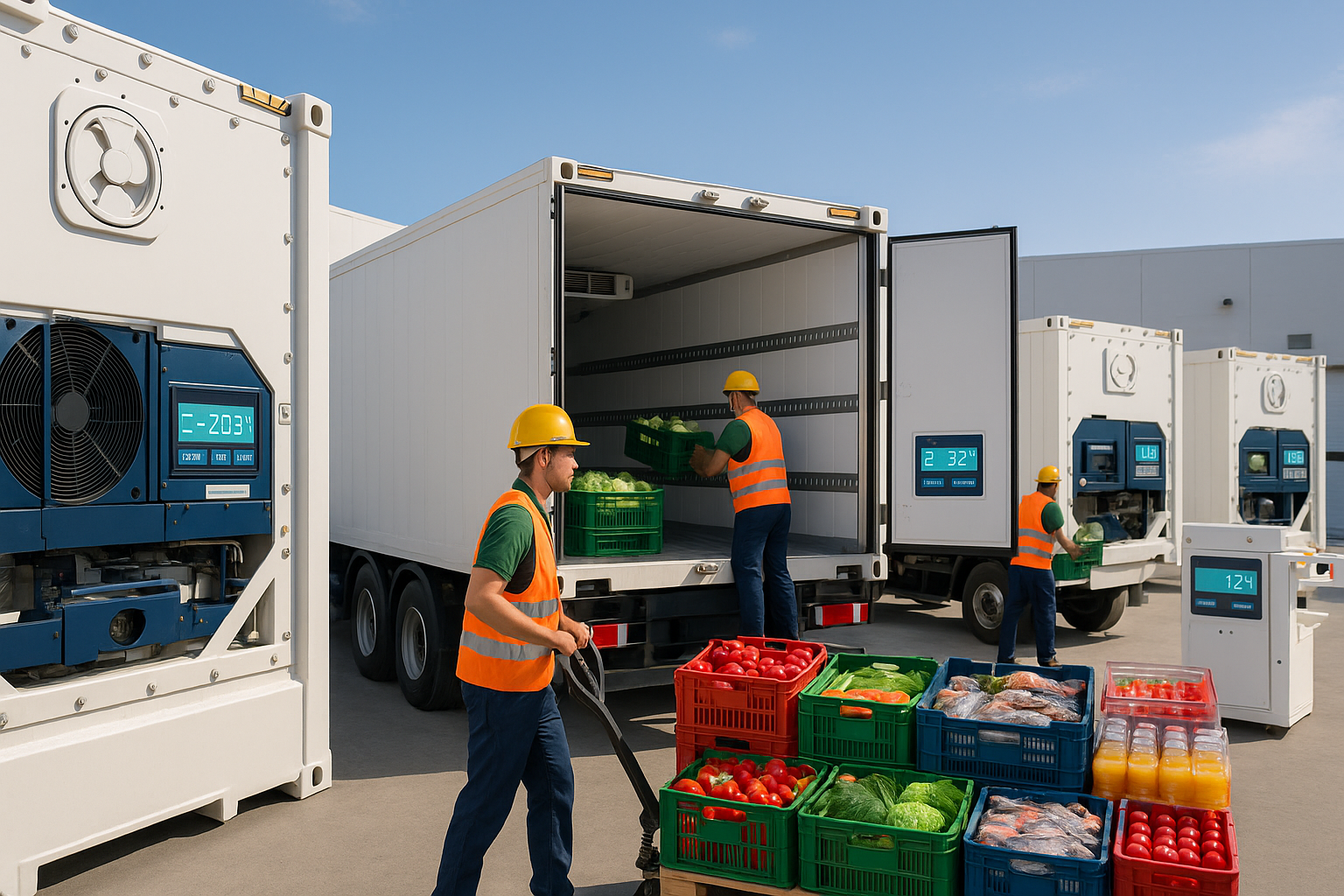

5. Specialized Storage for Different Food Categories
Different food and beverage products require unique temperature and humidity settings. Cold storage containers can be configured to suit specific needs:
- Frozen containers: Maintain subzero temperatures for meat, seafood, ice cream, and frozen meals.
- Chilled containers: Ideal for dairy, beverages, fresh produce, and bakery items.
- Dual-zone containers: Feature separate compartments for products requiring distinct temperature zones.
Some containers are also equipped with humidity control systems to protect moisture-sensitive items like leafy vegetables and certain fruits, preventing dehydration or condensation damage.
6. Compliance with Food Safety Regulations
Food safety regulations such as HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points), FDA Food Code, and ISO 22000 require strict temperature monitoring during transport and storage. Cold storage containers are designed to comply with these standards through integrated temperature data loggers, alarm systems, and remote monitoring technologies.
These systems allow operators to track conditions in real time, ensuring that any temperature deviation is detected and corrected immediately. Such traceability also provides valuable documentation for regulatory audits and quality assurance.
7. Integration with Smart Monitoring Systems
Digitalization has transformed cold chain logistics, and cold storage containers now often feature IoT-based monitoring and GPS tracking. These systems provide real-time updates on temperature, humidity, and location.
In the food and beverage industry, this level of visibility is critical. It allows logistics managers to:
- Detect temperature fluctuations early and take corrective action.
- Monitor door openings to prevent unauthorized access.
- Analyze transport performance and optimize energy usage.
Smart monitoring not only safeguards product integrity but also increases operational transparency and efficiency.
8. Energy-Efficient and Eco-Friendly Refrigeration Systems
Sustainability has become a major focus in the global food supply chain. Cold storage containers are evolving with energy-saving technologies such as variable-speed compressors, LED interior lighting, and low-GWP refrigerants like R452A or CO₂-based systems.
Some newer designs integrate solar panels or hybrid power sources, reducing diesel consumption and carbon emissions during operation. This helps companies meet environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals while cutting long-term operational costs.
9. Mobility and Rapid Deployment
A significant advantage of cold storage containers is their mobility. They can be transported by truck, rail, or ship and quickly deployed wherever needed—such as near production farms, seafood ports, or remote catering sites.
For example, in seafood or beverage logistics, containers can be stationed near coastal facilities or bottling plants to maintain continuous refrigeration from processing to shipping. This flexibility allows businesses to expand market reach while maintaining consistent cold chain conditions.
10. Role in Emergency and Event Catering Logistics
Cold storage containers are also widely used in temporary food operations such as outdoor events, festivals, and disaster relief efforts. They provide on-site refrigeration for beverages, prepared meals, or perishable supplies.
During emergencies, when power infrastructure may be limited, these containers can operate on generators or hybrid energy systems, ensuring uninterrupted cold storage for critical food supplies.
Conclusion
Cold storage containers are a cornerstone of modern food and beverage logistics. They combine precise temperature control, mobility, and scalability, enabling perishable goods to move safely through complex global supply chains. From preserving freshness to supporting sustainability goals, these containers offer reliable, efficient, and flexible solutions for today’s food distribution challenges.
As technology advances, smart systems, renewable energy integration, and improved insulation materials will further enhance their efficiency—paving the way for a greener and more resilient cold chain industry.