Content
- 1 Understanding Super Freezer Containers and Their Ultra-Low Temperature Capabilities
- 2 Key Applications Across Pharmaceutical and Biotech Industries
- 3 Premium Seafood Preservation and Marine Product Applications
- 4 Standard Cold Storage Container Applications and Industries
- 5 Technical Features and Advanced Refrigeration Systems
- 6 Container Sizes, Specifications, and Customization Options
- 7 Power Requirements and Energy Efficiency Considerations
- 8 Maintenance Best Practices and Operational Reliability
- 9 Cost Considerations and Return on Investment
- 10 Selecting the Right Cold Storage Solution for Your Needs
- 11 Future Trends in Portable Cold Storage Technology
Understanding Super Freezer Containers and Their Ultra-Low Temperature Capabilities
Super freezer containers represent the pinnacle of refrigeration technology in portable cold storage solutions. Unlike standard refrigerated containers that typically maintain temperatures between negative 25 degrees Celsius and positive 25 degrees Celsius, super freezer containers can achieve and sustain extreme temperatures ranging from negative 40 degrees Celsius down to negative 80 degrees Celsius. These specialized units utilize advanced cascade refrigeration systems, which employ two separate refrigeration circuits working in tandem with different refrigerants to safely protect temperature-sensitive cargo. The technology enables these containers to maintain pharmaceutical-grade cold storage conditions while remaining mobile and deployable across various locations.
The core distinction between super freezer containers and conventional cold storage units lies in their construction and cooling capacity. Super freezers incorporate enhanced insulation materials including vacuum panels, high-density polyurethane foam, and aerogel composites that dramatically reduce heat transfer. The refrigeration units feature powerful compressors rated to handle the extreme temperature demands, with evaporator fans specifically designed for high-pressure temperature drops. Additional safety features include escape hatches with integrated alarms, anti-slip flooring, internal lighting, and advanced monitoring systems that record temperature data every 15 minutes for regulatory compliance with FDA, EU GDP, and HACCP standards.
Key Applications Across Pharmaceutical and Biotech Industries
The pharmaceutical and biotechnology sectors rely heavily on super freezer containers for storing and transporting critical materials that require strict temperature control. Vaccine storage has become particularly crucial, with certain vaccines including COVID-19 inoculations requiring temperatures as low as negative 70 degrees Celsius to maintain efficacy. These containers provide the necessary cold chain infrastructure for vaccine distribution from manufacturing facilities to healthcare providers worldwide. Beyond vaccines, super freezers protect biological samples, blood plasma, white blood cells, red blood cells, skin grafts, and bone tissue used in transplantation and medical research.
Research and development operations benefit significantly from super freezer technology. Laboratories store research materials, compound samples, and validation testing components for industries ranging from automotive and aerospace to wind power and offshore oil and gas applications. The containers enable scientific institutions, bioengineering facilities, and university laboratories to maintain cryogenic storage conditions without investing in permanent infrastructure. The portability factor allows research teams to deploy ultra-low temperature storage wherever needed, supporting field studies and remote testing operations. Biotechnology companies utilize these units for preserving bacterial cultures, semen samples for reproductive research, and sensitive electronic components that require specific low-temperature storage protocols.
Premium Seafood Preservation and Marine Product Applications
The high-value seafood industry depends on super freezer containers to preserve the quality and market value of premium catches. Sashimi-grade tuna, blue-fin tuna, swordfish, salmon, sea urchin, and other delicate marine products require immediate flash freezing to maintain their first-day freshness and achieve Grade A classification. At temperatures between negative 60 and negative 70 degrees Celsius, microbial decomposition ceases completely, ensuring that seafood arrives at destinations across the globe in perfect condition even after extended storage periods. This capability provides an environmentally friendly and cost-effective alternative to expensive air freight shipments.
Offshore fishery companies and tuna processing operations utilize super freezers both onboard vessels and at processing facilities. The containers can be deployed on ships for ocean transport or placed at dock facilities for temporary storage before distribution. The ability to maintain ultra-low temperatures in tropical climates without requiring dry ice top-offs or liquid nitrogen systems makes these units particularly valuable for marine operations. Processors can store freshly caught fish, crab, and processed seafood products while maintaining the cellular structure and flavor profiles that command premium prices in international markets. The cascade refrigeration technology ensures consistent temperature control regardless of ambient conditions or door access cycles.
Standard Cold Storage Container Applications and Industries
Cold storage containers serve a broader range of industries requiring temperature-controlled environments for perishable goods. The food and beverage sector represents the largest user base, with applications spanning fresh produce storage, frozen meat and poultry preservation, dairy product distribution, and beverage cooling. Restaurants and catering operations rely on refrigerated containers for storing large quantities of ingredients, especially during peak seasons, special events, or when traditional refrigeration capacity proves insufficient. Agricultural businesses use these units to preserve harvested crops before distribution, maintaining product quality during market fluctuations and preventing spoilage during transportation delays.
Retail operations including grocery stores, supermarkets, and distribution centers employ cold storage containers to manage overflow inventory and seasonal stock demands. The flexibility of portable refrigeration allows businesses to expand cold storage capacity without constructing permanent facilities. Event management companies utilize refrigerated containers for weddings, festivals, outdoor markets, and large gatherings where temporary food storage becomes essential. The pharmaceutical industry extends beyond ultra-low freezers to standard cold storage for medications requiring temperatures between 2 and 8 degrees Celsius, medical supplies, and temperature-sensitive diagnostic materials. Chemical industries store materials requiring specific temperature ranges for stability and safety, while the brewing and winemaking sectors maintain controlled fermentation temperatures and long-term product storage.
Emerging Applications in Technology and Industrial Sectors
Technology industries increasingly utilize cold storage containers for specialized applications. Data centers employ refrigerated units for cooling sensitive server equipment and maintaining optimal performance conditions. Electronics manufacturing requires temperature-controlled storage for semiconductors, batteries undergoing testing, and phase-changing materials used in advanced applications. The petrochemical industry uses refrigeration systems for gas separation, condensation processes, dehumidification, and solvent recovery operations. Paper manufacturing facilities maintain cooling systems for specific production stages, while forensic medical facilities require cold storage for biological evidence and specimen preservation.
Technical Features and Advanced Refrigeration Systems
Modern cold storage containers incorporate sophisticated refrigeration technology designed for reliability and energy efficiency. The cascade refrigeration system in super freezers utilizes two independent circuits with different refrigerants, managed by advanced controllers that optimize performance while minimizing energy consumption. Standard refrigerated containers employ compression refrigeration systems with evaporative cooling, while some specialized units integrate alternative technologies including thermoelectric cooling based on the Peltier effect and Stirling cycle cooling using cyclic compression and expansion of gas. These systems include automatic hot-gas defrost cycles occurring every 6 to 12 hours depending on humidity levels and door access frequency.
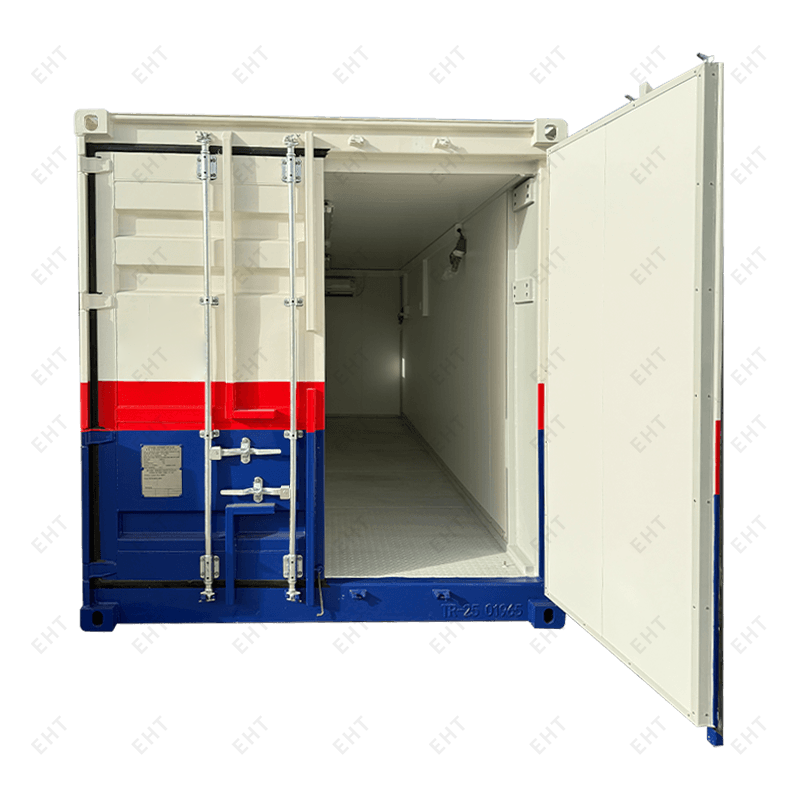
Insulation technology represents a critical component of container performance. Super freezer units feature multilayer insulation systems combining vacuum panels that eliminate air-based heat transfer, high-density polyurethane foam with exceptional thermal resistance, and specialized aerogel materials with extremely low thermal conductivity. The walls, roof, and floor incorporate significantly thicker insulation compared to standard containers, often requiring increased external height to accommodate the enhanced insulation while maintaining interior capacity. Corrugated ribs and internal columns reinforce structural integrity, while stepped door designs with multiple rubber seals prevent heat leakage. All steel components undergo shot-blasting to Swedish Standard SA 2.5, with specialized foam adhesives applied to contact surfaces for optimal bonding with polyurethane insulation.
Monitoring and Control Systems
Advanced monitoring systems enable precise temperature control and regulatory compliance. Containers feature microprocessors that record temperature readings every 15 minutes, creating verifiable data logs for auditing purposes. Remote monitoring capabilities allow operators to track temperature, receive real-time alerts for deviations, and troubleshoot systems through GSM communication networks. Temperature sensors distributed throughout the container ensure uniform cooling, while alarm systems notify personnel immediately when conditions exceed preset parameters. Many units include backup power options and redundant refrigeration systems that provide additional security for high-value cargo, ensuring continuous operation even during primary system maintenance or power fluctuations.
Container Sizes, Specifications, and Customization Options
Cold storage containers are available in standard ISO shipping container sizes to facilitate seamless integration with existing logistics infrastructure. Common configurations include 10-foot, 20-foot, and 40-foot lengths, with standard widths of 8 feet and heights of 8 feet 6 inches. High-cube variants offer 9 feet 6 inches of external height, providing additional interior headroom for tall cargo or enhanced insulation thickness. A 20-foot container typically offers 28 to 30 cubic meters of storage capacity, while 40-foot units provide 56 to 60 cubic meters. The standard ISO dimensions allow containers to be lifted via twist-locks, transported on tilt-bed trucks, loaded onto ships, and positioned at marine terminals using conventional handling equipment.
Customization options enable businesses to tailor containers to specific operational requirements. Interior modifications include flat or T-floor configurations, internal shelving systems for organized storage, adjustable ceiling fans for improved air circulation, and specialized lighting systems. Safety enhancements encompass escape hatches accessible only from inside for worker protection, man-trapped alarms, emergency stop buttons, and vacuum valves for pressure equalization. Exterior modifications may include mounting brackets for securing containers to foundations, connection ports for linking multiple units, and specialized paint coatings offering enhanced corrosion resistance. Dual refrigeration systems provide built-in redundancy for critical applications, while blast-freeze functionality allows rapid temperature reduction for specific products requiring quick freezing protocols.
Power Requirements and Energy Efficiency Considerations
Cold storage containers require reliable electrical power to maintain temperature control. Standard refrigerated units typically operate on 230-volt three-phase or 460-volt three-phase power systems, while super freezers designed for seagoing transport can accommodate 360 to 500-volt power at 50 or 60 Hertz frequencies. Land-based installations connect to grid power through standard electrical service, with many facilities dedicating circuits specifically for refrigeration units to ensure consistent supply. The startup current demand for compressor motors requires adequate amperage capacity, with super freezer units often needing 40 kilovolt-ampere minimum from continuous-run diesel generators for off-grid applications.
Energy efficiency has become a priority as operational costs and environmental sustainability gain importance. Modern containers incorporate energy-saving features including advanced compressor technology that optimizes power consumption while maintaining cooling capacity, high-efficiency insulation that reduces the frequency of cooling cycles, and smart controllers that adjust refrigeration based on actual load conditions. Some installations utilize solar panel systems paired with battery storage for remote locations, while hybrid systems combine solar power with generator backup to ensure uninterrupted operation. The reduced energy consumption not only lowers operational costs but also minimizes the environmental impact of cold storage operations, aligning with sustainability initiatives across industries.
Maintenance Best Practices and Operational Reliability
Preventive maintenance programs are essential for ensuring reliable operation and extending container lifespan. Regular inspections should occur quarterly for business-critical applications, with monthly walk-throughs recommended for continuous cold storage operations. Key inspection points include checking the evaporator for proper air temperature, unusual sounds indicating mechanical issues, and signs of water or oil leakage. The condenser requires monthly quality checks, with properly functioning units showing cooler pipes at the refrigerant outlet compared to inlet temperatures. Electrical connections need verification to ensure proper current flow, with electricians addressing any faults in wiring or replacing failed fuses immediately to prevent system interruptions.
Cleaning protocols maintain sanitation standards and prevent contamination. Interior and exterior surfaces should be washed with non-corrosive cleaning agents designed for cold storage environments. Floor channels require regular debris removal to support proper airflow, while drain lines and drip trays need cleaning to prevent mold growth and clogs. During defrost operations, products should be temporarily moved to backup units, with the container powered down and doors opened to allow warming. Towels placed around the floor absorb melted frost, and warm water with light detergent cleans interior surfaces without allowing moisture to enter refrigeration or electrical compartments. Temperature sensors require calibration checks every two years using certified RTD or thermocouple instruments to ensure display accuracy matches actual conditions.
Documentation and Compliance Requirements
Maintaining detailed records creates operational accountability and facilitates problem diagnosis. Documentation should include logs of all maintenance activities, temperature monitoring data, calibration certificates, and service reports. These records prove essential for regulatory compliance in pharmaceutical and food industries, where authorities require verifiable evidence of proper storage conditions. Many containers arrive with GDP certification documentation, HACCP compliance verification, and validation protocols. Facilities should implement standard operating procedures for loading, unloading, temperature excursion handling, and emergency response. Regular review and updating of procedures ensures alignment with industry best practices and regulatory requirements.
Cost Considerations and Return on Investment
Purchasing cold storage containers represents a significant capital investment, with costs varying based on size, temperature capabilities, and features. Standard 20-foot refrigerated containers generally cost less than super freezer units due to simpler refrigeration systems and standard insulation. A 40-foot super freezer with cascade refrigeration and ultra-low temperature capability typically commands premium pricing, often reaching $65,000 or more depending on specifications and customization. However, this investment costs a fraction of constructing permanent cold storage facilities, which require extensive building permits, concrete foundations, specialized construction, and ongoing property taxes.
The return on investment includes both direct cost savings and operational advantages. Businesses avoid expensive air freight costs by utilizing sea transport with reliable temperature control, reduce product loss through consistent storage conditions, and gain flexibility to redeploy assets as market needs change. Containers remain movable assets that can be relocated, rented to other operations during low-demand periods, or sold if requirements change. Rental options provide alternatives for seasonal needs, special projects, or businesses wanting to avoid capital expenditure. Many suppliers offer both purchase and rental arrangements, with rental agreements including delivery, pickup services, and maintenance support that simplifies logistics and reduces management burden.
Selecting the Right Cold Storage Solution for Your Needs
Choosing appropriate cold storage equipment requires careful assessment of specific business requirements. Temperature range represents the primary consideration, with super freezers necessary for applications requiring temperatures below negative 40 degrees Celsius, while standard refrigerated containers suffice for most food storage, pharmaceutical distribution, and general cold chain applications operating between negative 25 and positive 25 degrees Celsius. Storage volume needs determine container size, with businesses balancing available space, product quantity, and access requirements. A 20-foot container fits in standard parking spaces and accommodates smaller operations, while 40-foot units maximize storage efficiency for high-volume applications.
Additional factors include placement requirements such as dock-level versus ground-level access, indoor versus outdoor installation, and proximity to power sources. Regulatory compliance needs vary by industry, with pharmaceutical and medical applications requiring GDP certification, temperature validation, and comprehensive monitoring systems. Budget constraints influence decisions between purchasing new units, acquiring used containers, or establishing rental agreements. Working with experienced cold storage providers offers advantages including technical expertise, installation support, maintenance services, and regulatory guidance. Reputable suppliers provide calibration certificates, installation assistance, operator training, and ongoing service support that helps businesses maximize their investment while ensuring reliable temperature control for valuable inventory.
Future Trends in Portable Cold Storage Technology
The portable cold storage industry continues evolving with technological advancements addressing efficiency, sustainability, and monitoring capabilities. Refrigerant technology improvements focus on environmentally friendly alternatives that reduce global warming potential while maintaining cooling performance. Smart monitoring systems integrate with Internet of Things platforms, enabling predictive maintenance through data analytics that identify potential failures before they occur. Machine learning algorithms optimize refrigeration cycles based on usage patterns, reducing energy consumption while maintaining precise temperature control. Battery storage technology advances allow containers to maintain temperature during temporary power interruptions without requiring immediate generator backup.
Sustainability initiatives drive development of solar-powered refrigeration systems, improved insulation materials with higher thermal resistance and lower environmental impact, and modular designs that facilitate easier repairs and component replacement. The growing demand for vaccine distribution, biotechnology research, and premium food products continues expanding the market for ultra-low temperature storage solutions. Integration with blockchain technology enables immutable temperature records throughout supply chains, providing enhanced transparency for regulatory compliance and quality assurance. As cold chain requirements become more stringent across industries, portable cold storage containers will remain essential infrastructure supporting global trade, medical advancement, and food security.